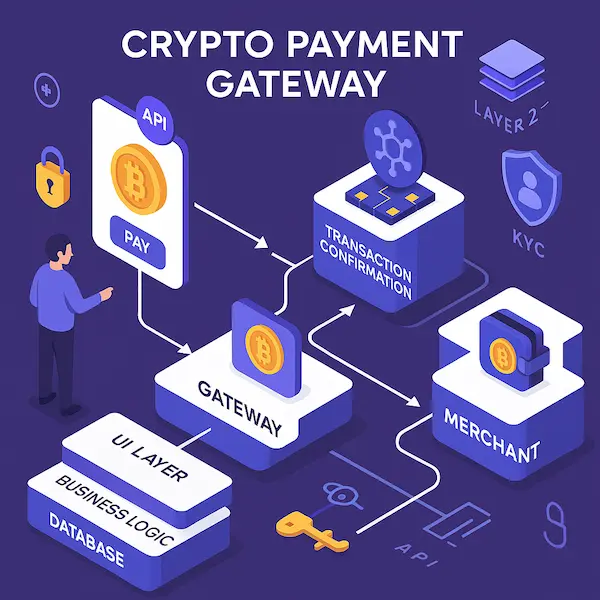
The world of digital payment is changing fast and cryptocurrency has proved to be revolutionizing digital payment. Since companies are becoming more interested in the need to accept or use digital currencies, the need to develop custom crypto payment gateways increased dramatically. To the developers of this venture, it is important to study complexities and needs of this venture prior to developing it.
The crypto payment gateways act as the intermediaries between the protean and the blockchain networks where the smooth exchange of cryptocurrencies can take place. Crypto gateways have to work with the peculiarities of blockchain technology, unlike conventional payment processors that process fiat payments, where one does not have to juggle with network confirmations, wallet integration, and volatility, among other dynamics.

Contents
- 1 Understanding Custom Crypto Payment Gateway Architecture
- 2 Technical Requirements and Blockchain Integration
- 3 Regulatory Compliance and Legal Framework
- 4 Development Challenges and Solutions
- 5 Integration Testing and Quality Assurance
- 6 Advanced Features and Future Considerations
- 7 Cost Analysis and Business Considerations
- 8 Merchant Integration and User Experience
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Custom Crypto Payment Gateway Architecture
Core Components of a Payment Gateway
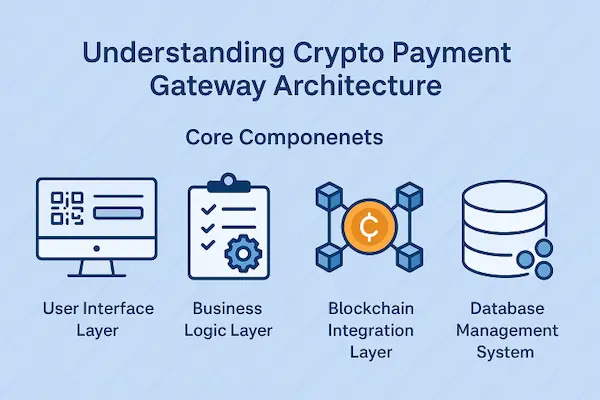
When you develop custom crypto payment gateway infrastructure, a number of crucial elements interact, making the system operational. Architecture is generally made up of user interface layer, business logic layer, blockchain integration layer and database management system.
Customer interactions are accessed through the user interface that presents payment options, QR codes, and updates on the status of the transactions. The business logic layer receives payment requests, performs exchanging rates calculation and correlates transactions flow. The layer of integrating block chains has direct communication with different cryptocurrency networks, and the database stores the records of transactions, the identity of the user, and the configuration.
The custom crypto payment gateway of the modern world are expected to embrace more than one blockchain network at the same time, making the architecture of such products highly burdensome as it is required to accommodate various protocols and consensus methods.
Transaction Flow Process
Understanding the complete transaction flow is fundamental when developing a custom crypto payment gateway. The process begins when a customer initiates a payment, triggering the gateway to generate a unique wallet address or payment request. The system then monitors the blockchain for incoming transactions to that specific address.
| Stage | Description | Time Frame |
| Payment Initiation | Customer selects crypto payment option | Instant |
| Address Generation | Gateway creates unique receiving address | 1-2 seconds |
| Payment Broadcasting | Customer sends cryptocurrency to address | Varies by network |
| Confirmation Waiting | System monitors for network confirmations | 10 minutes – 1 hour |
| Settlement | Funds confirmed and merchant credited | After confirmations |
Once the transaction receives sufficient network confirmations, the gateway credits the merchant’s account and updates the order status. This entire process requires careful monitoring and error handling to ensure reliability.
Technical Requirements and Blockchain Integration
Supported Cryptocurrencies and Networks
A comprehensive custom crypto payment gateway must support multiple cryptocurrencies and blockchain networks. Bitcoin remains the most popular option, but Ethereum, Litecoin, Bitcoin Cash, and various altcoins are increasingly demanded by merchants and customers.
Each blockchain network has unique characteristics that affect integration complexity. Bitcoin uses UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model, while Ethereum employs an account-based system with smart contract capabilities. Developers must understand these fundamental differences to implement proper wallet management and transaction handling.
Building a custom crypto payment gateway requires maintaining separate wallet infrastructures for each supported cryptocurrency. This includes generating addresses, managing private keys, and implementing appropriate security measures for different cryptographic algorithms.
API Integration and Wallet Management
Robust API design is crucial for merchant integration and system scalability. The gateway API should provide endpoints for payment creation, status checking, webhook notifications, and administrative functions. RESTful API design with proper authentication and rate limiting ensures secure and efficient communication.
Wallet management represents one of the most critical aspects of gateway development. Hot wallets facilitate immediate transactions but pose security risks, while cold wallets offer enhanced security at the expense of convenience. Most production systems implement a hybrid approach, maintaining small amounts in hot wallets for instant processing while storing larger reserves in cold storage.
Security Considerations
Security cannot be an afterthought when developing cryptocurrency payment systems. Multi-signature wallets, hardware security modules (HSMs), and encrypted key storage are essential components of a secure architecture.
Key Security Measures:
• Multi-signature wallet implementation
• Regular security audits and penetration testing
• Encrypted communication channels (TLS/SSL)
• Two-factor authentication for administrative access
• Regular key rotation and backup procedures
• Compliance with industry security standards
Private key management deserves special attention, as compromised keys can result in irreversible fund loss. Implementing proper key generation, storage, and rotation procedures is non-negotiable for production systems.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Framework
Understanding Financial Regulations
Cryptocurrency payment processing operates in a complex regulatory environment that varies significantly by jurisdiction. In the United States, crypto businesses must comply with FinCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network) regulations, including anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements.
Developers must research and understand the specific regulatory requirements in their target markets before deployment. Some jurisdictions require money transmitter licenses, while others have specific cryptocurrency business registration requirements.
Compliance Implementation
Implementing compliance features requires careful planning and ongoing maintenance. KYC procedures typically involve identity verification, document collection, and risk assessment. AML compliance includes transaction monitoring, suspicious activity reporting, and sanctions screening.
| Compliance Requirement | Implementation Approach | Ongoing Maintenance |
| KYC Verification | Identity document scanning, facial recognition | Regular updates to verification databases |
| AML Monitoring | Real-time transaction analysis, pattern recognition | Continuous rule updates and false positive management |
| Sanctions Screening | Database comparison against OFAC lists | Daily database updates and re-screening |
Many developers choose to integrate third-party compliance services rather than building these features from scratch, as maintaining up-to-date regulatory compliance requires specialized expertise and resources.
Development Challenges and Solutions
Handling Network Congestion and Fees
Blockchain networks experience varying levels of congestion, affecting transaction confirmation times and fees. During high-demand periods, Bitcoin and Ethereum networks can become expensive and slow, impacting user experience and merchant operations.
Smart fee estimation algorithms help optimize transaction costs while maintaining reasonable confirmation times. Dynamic fee adjustment based on network conditions ensures transactions remain competitive without overpaying during low-congestion periods.
Managing Cryptocurrency Volatility
Price volatility presents unique challenges for crypto payment processing. A payment worth $100 in Bitcoin at initiation might be worth significantly more or less by the time it confirms on the blockchain. This volatility risk affects both merchants and payment processors.
Several strategies address volatility concerns:
- Instant conversion: Automatically convert received cryptocurrency to stablecoins or fiat currency
- Hedging mechanisms: Use derivatives or futures contracts to offset price risk
- Dynamic pricing: Adjust payment amounts in real-time based on current exchange rates
- Timeout periods: Set expiration times for payment requests to limit exposure
Scalability and Performance Optimization
As transaction volumes grow, payment gateways must scale efficiently to handle increased load. Database optimization, caching strategies, and microservices architecture help maintain performance under heavy usage.
Implementing proper monitoring and alerting systems enables proactive identification of performance bottlenecks and system issues. Load balancing and redundancy ensure high availability even during peak usage periods.
Integration Testing and Quality Assurance
Testnet Development and Simulation
Thorough testing is essential before deploying cryptocurrency payment systems to production. Most blockchain networks provide testnet environments that mirror mainnet functionality without using real funds. Developers should extensively test all payment scenarios, error conditions, and edge cases on testnets.
Creating comprehensive test suites that cover various transaction types, network conditions, and failure scenarios helps identify potential issues before they affect real transactions. Automated testing frameworks should include unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end transaction simulations.
Security Auditing and Penetration Testing
Professional security audits should be conducted before launching any custom crypto payment gateway. These audits examine code quality, identify potential vulnerabilities, and assess overall system security. Penetration testing specifically targets the gateway’s defenses against malicious attacks.
Regular security assessments should continue after launch, as new vulnerabilities and attack vectors are constantly discovered. Bug bounty programs can provide ongoing security validation from the broader security community.
Advanced Features and Future Considerations
Smart Contract Integration
Modern custom crypto payment gateway increasingly incorporate smart contract functionality, particularly on platforms like Ethereum. Smart contracts can automate complex payment logic, enable programmable payments, and provide additional security guarantees.
Implementing smart contract features requires understanding of blockchain programming languages like Solidity, gas optimization techniques, and contract upgrade strategies. Smart contracts also introduce additional testing requirements and potential attack vectors that must be carefully considered.
Multi-Chain Support and Interoperability
The cryptocurrency ecosystem is becoming increasingly multi-chain, with various blockchain networks offering different advantages. Payment gateways that support multiple chains provide more options for merchants and customers while increasing technical complexity.
Cross-chain protocols and bridge technologies enable interoperability between different blockchain networks. However, these technologies are still evolving and may introduce additional risks and complexities.
| Blockchain Network | Average Confirmation Time | Typical Transaction Fee | Smart Contract Support |
| Bitcoin | 10-60 minutes | $1-$50 (varies with congestion) | Limited (scripting) |
| Ethereum | 1-5 minutes | $2-$100 (varies with gas price) | Full support |
| Litecoin | 2.5-15 minutes | $0.01-$0.10 | Limited |
| Bitcoin Cash | 10-60 minutes | $0.01-$0.05 | Limited |
| Polygon | 2-5 seconds | $0.001-$0.01 | Full support |
Lightning Network and Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 2 scaling solutions like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and various Ethereum L2 solutions offer faster, cheaper transactions. Integrating these technologies can significantly improve user experience but requires additional technical expertise and infrastructure.
Lightning Network integration involves managing payment channels, routing payments through the network, and handling channel liquidity. While complex, Lightning can enable near-instant Bitcoin payments with minimal fees.
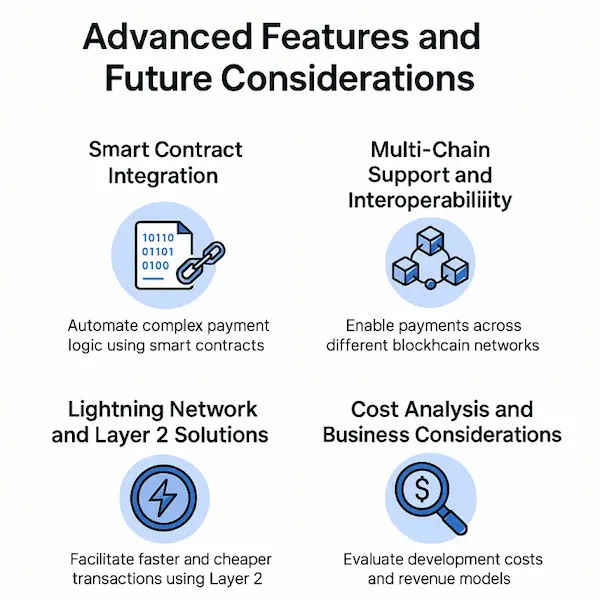
Cost Analysis and Business Considerations
Development and Operational Costs
Building a custom crypto payment gateway involves significant upfront development costs and ongoing operational expenses. Initial development typically requires 6-12 months with a experienced development team, depending on feature complexity and supported cryptocurrencies.
Key cost considerations include:
- Development team salaries and contractor fees
- Security audits and compliance consulting
- Infrastructure hosting and monitoring
- Third-party service integrations
- Legal and regulatory compliance
- Ongoing maintenance and updates
Revenue Models and Monetization
Custom Crypto payment gateway typically generate revenue through transaction fees, ranging from 0.5% to 3% per transaction. Additional revenue streams include subscription fees for premium features, exchange rate margins, and value-added services like compliance tools or analytics.
Competitive fee structures are essential for merchant adoption, but developers must balance affordability with sustainability. Understanding the target market’s price sensitivity and competitive landscape helps optimize pricing strategies.
Empower your business with XaiGate, the next-generation best crypto payment gateway designed to simplify digital payments and drive global commerce.
Merchant Integration and User Experience
API Design and Documentation
Well-designed APIs and comprehensive documentation are crucial for successful merchant adoption. RESTful API design principles, clear error handling, and extensive code examples help developers integrate the payment gateway quickly and reliably.
Providing software development kits (SDKs) for popular programming languages and e-commerce platforms significantly reduces integration barriers. WordPress plugins, Shopify apps, and other platform-specific integrations expand the potential merchant base.
Customer Support and Troubleshooting
Cryptocurrency transactions can be confusing for end users, making excellent customer support essential. Support systems should handle common issues like delayed confirmations, incorrect addresses, and transaction status inquiries.
Automated support features like transaction lookup tools, FAQ systems, and status pages reduce support burden while providing immediate assistance to users. Escalation procedures ensure complex issues receive appropriate attention from technical staff.
Conclusion
The process of creating an individual crypto fork of the payment gateway is an essential technical and business venture that implies thorough planning, large amounts of resources, and consistent effort. The difficulty of the blockchain integration, regulatory issues, and security force makes this project acceptable only to professional developers who have strong enough business needs that could not be satisfied by the existing options.
Developers must do a lot of research before deciding to develop a custom crypto payment gateway, including going through existing third-party gateway services, comparing their technical abilities, and having a sufficient budget to support the development process and maintenance in the long term. This industry of cryptocurrency payment is fast growing and thus it has been necessitating constant adjustments and advancements to cope with the running way of business.
Technical excellence is one of the factors needed to succeed in this space along with the knowledge of the market needs and requirements, and understanding the expectations of the users. Although the issues to be overcome are great, the increased acceptance of cryptocurrency payments draws big opportunities to effectively execute solutions focusing on security, compliance, and user experience.
In most companies, it will be more viable to work with experienced payment gateway services or utilize third-party obtained solutions instead of making a custom-developed structure. Nevertheless, to organizations which have particular needs, resources and technical knowledge, developing a tailored custom crypto payment gateway may allow them to gain competitive advantages and a full control over the payment process.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long does it typically take to build a custom crypto payment gateway from scratch?
Building a comprehensive custom crypto payment gateway typically takes 6-12 months with an experienced development team. Simple implementations might be completed in 3-4 months, while enterprise-grade solutions with extensive features can take 12-18 months or longer.
2. What are the most important security considerations for custom crypto payment gateways?
Key security considerations include secure private key management, multi-signature wallet implementation, encrypted communications, regular security audits, compliance with industry standards, and proper access controls. Private key security is absolutely critical as compromised keys can result in irreversible fund loss.
3. Do I need special licenses to operate a custom crypto payment gateway?
Licensing requirements vary by jurisdiction. In the United States, you may need money transmitter licenses in various states, FinCEN registration, and compliance with AML/KYC regulations. International operations require understanding local cryptocurrency regulations in each target market.
4. How do custom crypto payment gateways handle price volatility?
Common strategies include instant conversion to stablecoins or fiat currency, implementing hedging mechanisms, using dynamic pricing that adjusts in real-time, and setting timeout periods for payment requests to limit exposure to price fluctuations.
5. What’s the difference between building a gateway versus using existing solutions?
Building custom solutions provides complete control and customization but requires significant resources, technical expertise, and ongoing maintenance. Using existing solutions is faster and often more cost-effective but may have limitations in customization and feature availability.
6. Which cryptocurrencies should I support in my payment gateway?
Bitcoin and Ethereum are essential for most gateways due to high adoption rates. Additional popular options include Litecoin, Bitcoin Cash, and major stablecoins like USDC and USDT. The specific selection should be based on your target market’s preferences and technical requirements.
7. What is a custom crypto payment gateway and how is it different from standard options?
A custom crypto payment gateway is a tailored solution built specifically for a business’s needs, unlike standard gateways which offer fixed features. It provides more flexibility, control, and integration options.
8. Why would a company choose to build a custom crypto payment gateway instead of using existing platforms?
Companies with unique operational needs, regulatory requirements, or branding preferences may opt for a custom gateway to gain full control over the user experience and backend infrastructure.
9. How secure is a custom crypto payment gateway compared to third-party solutions?
Security depends on implementation, but a well-built custom crypto payment gateway can offer superior protection through features like multi-sig wallets, cold storage, and private key encryption—assuming best practices are followed.
10. Do I need a development team to maintain a custom crypto payment gateway?
Yes, maintaining a custom solution requires ongoing technical expertise. This includes updating APIs, monitoring blockchain integrations, and handling security audits.
For daily updates, subscribe to XAIGATE’s blog!
We may also be found on GitHub, and X (@mxaigate)! Follow us!